Z-Score Calculator
Determine the standardized position of any data point within a normal distribution.
Z-score: —
Z-score ↔ Probability Converter
P(x < Z)
—
—
P(x > Z)
—
—
P(0 < x < Z)
—
—
P(-Z < x < Z)
—
—
P(x < -Z or x > Z)
—
—
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Enter the raw score (observed value)
-
Enter the population mean (μ)
-
Enter the population standard deviation (σ)
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
- Using sample standard deviation when population σ is required.
- Forgetting to subtract the mean - z-score becomes meaningless.
- Thinking z-score > 3 is impossible - just very rare.
- Mixing up raw score with standardized score in further calculations.
Practical Applications📊
Standardizing test scores (SAT, GRE, IQ) for fair comparison across different versions
Detecting outliers in research datasets and quality-control monitoring
Calculating probabilities and percentiles in normally distributed variables
Questions and Answers
What is a z-score in statistics?
A z-score represents the distance of a raw score from the population mean expressed in units of the population standard deviation. It transforms any normal distribution into the standard normal distribution, enabling the use of standardized tables and probability calculations.
How to calculate z-score manually?
Subtract the population mean from the observed value and divide the result by the population standard deviation. The formula z = (x − μ) / σ is applied universally when population parameters are available. Online calculators perform this operation instantly and eliminate arithmetic errors.
How to find z-score when mean and standard deviation are known?
With the raw score (x), population mean (μ) and population standard deviation (σ) available, direct substitution into the z-score formula yields the standardized value. This approach is standard in inferential statistics and hypothesis testing.
What does a negative z-score indicate?
A negative standard score shows that the original data point lies below the population mean. For example, a standard score of −1.5 means the value is 1.5 standard deviations below the average of the distribution.
How is z-score used to find probability?
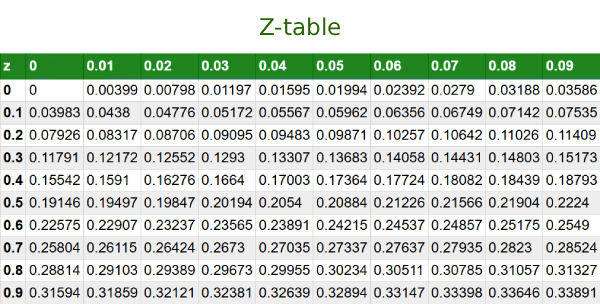
After obtaining the z-score, refer to the standard normal distribution table (z-table) or cumulative distribution function to determine the area under the curve. This area corresponds to the probability of observing a value less than or equal to the standardized score.
What formula does this z-score calculator use?
The calculator applies the standard z-score formula: $z = \frac{x - \mu}{\sigma}$, where $x$ is the raw score, $\mu$ is the population mean, and $\sigma$ is the population standard deviation. This formula remains the cornerstone of normalization in statistical analysis.
How should z-score results be interpreted?
A z-score of 0 places the observation exactly at the population mean. Approximately 68% of data fall within ±1, 95% within ±2, and 99.7% within ±3 standard deviations in a normal distribution. Larger absolute values indicate increasingly rare observations relative to the given population.
Disclaimer: This calculator is designed to provide helpful estimates for informational purposes. While we strive for accuracy, financial (or medical) results can vary based on local laws and individual circumstances. We recommend consulting with a professional advisor for critical decisions.