Remainder Calculator
Compute precise integer quotients and remainders. Our engine implements the Euclidean Division Theorem for consistent results across all integer sets.
Remainder: -
Quotient (integer): -
Quotient (decimal): -
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Identify the dividend (numerator) and the divisor (denominator).
-
Input integers into the fields (supports negative and large values).
-
Analyze the output to distinguish between the integer quotient and the residual remainder.
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
- Divisor of Zero: Division by zero is undefined in all algebraic systems and will return an error.
- Inputting Decimals: This tool is optimized for Integer Arithmetic; for decimals, standard division is more appropriate.
- Modulo vs. Remainder: Be aware that some programming languages (like C++ or Java) handle negative remainders differently than the Euclidean standard used here.
Advanced Practical Applications📊
Algorithm Verification: Test modulo (%) logic for software development and cyclic data structures.
Number Theory: Solve problems related to congruence relations and modular arithmetic.
Cryptography: Verify integer partitions and shifts in basic encryption algorithms.
Education: Validate long division steps and the Remainder Theorem for polynomial preparation.
Questions and Answers
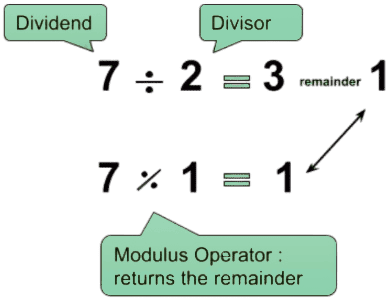
What is the difference between a remainder and a modulo?
In mathematics, they are often identical. However, in computing, "remainder" can be negative depending on the language, while "modulo" usually follows the cyclic positive-only rule used by this calculator.
How does the calculator handle negative numbers?
We follow the Euclidean definition. If you divide $-25$ by $7$, the calculator finds a quotient of $-4$ and a remainder of $3$, because $7 \times (-4) + 3 = -25$. This ensures the remainder is always $r \ge 0$.
Is this tool suitable for large-scale integer division?
Yes. Our engine uses BigInt processing, allowing you to calculate remainders for astronomical numbers that would cause overflow errors on standard handheld calculators.
Why does a standard calculator show a decimal instead?
Handheld calculators perform "floating-point" division. To convert a decimal (like 3.5) to a remainder, you take the decimal part (0.5) and multiply it by the divisor.
What are the applications of remainders in computer science?
Remainders (modulo) are used in Hash Tables, determining leap years, handling array indices in circular buffers, and in various CSS styling rules (nth-child).
Disclaimer: This calculator is designed to provide helpful estimates for informational purposes. While we strive for accuracy, financial (or medical) results can vary based on local laws and individual circumstances. We recommend consulting with a professional advisor for critical decisions.