Hex Calculator
Handle hexadecimal arithmetic and convert between decimal and hex numbers.
Hex Calculator
Decimal → Hex
Hex → Decimal
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Enter the first number in hex or decimal format.
-
Select the arithmetic operation or leave blank for conversion.
-
Click Calculate to view results in both number systems.
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
- Using invalid characters like G or Z in hexadecimal inputs.
- Applying base-10 carry rules instead of base-16 (carrying at 16).
- Confusing the order of remainders when converting decimal to hex manually.
- Ignoring signed two's complement context in hex arithmetic.
Practical Applications📊
Calculate memory offsets and pointer addresses in low-level programming.
Convert RGB values to hex color codes for web design and CSS.
Verify bitwise operations and data encoding in computer science tasks.
Perform fast hex to integer checks during firmware debugging.
Questions and Answers
What is a hex calculator?
A hex calculator is a specialized tool designed to perform arithmetic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, directly in base 16. Beyond basic math, it serves as a bridge between number systems, allowing users to convert hexadecimal values to decimal and vice versa. This is critical for tasks in computer science, where hex is used to represent everything from memory addresses to color codes in web design.
How does hex addition work?
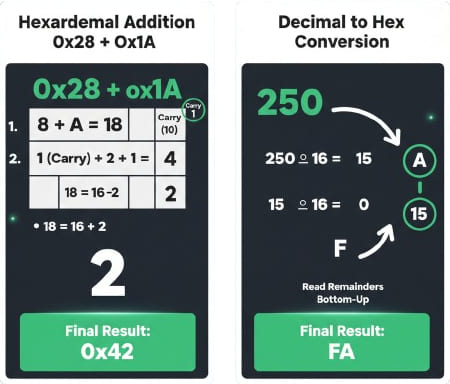
Hexadecimal addition follows a column-by-column logic similar to decimal math, but with a threshold of 16. You add the digits in a column; if the sum is 15 or less, you write it down (using A-F for 10-15). If the sum is 16 or greater, you subtract 16, write down the remainder, and carry 1 to the next column. For example, $F + 1$ results in $0$ with a carry of $1$, written as $10_{16}$ (which equals 16 in decimal).
How to convert decimal to hex?
To convert a decimal number to hex, you use the repeated division method. Divide the decimal integer by 16 and record the remainder. Continue dividing the quotient by 16 until it reaches zero. The remainders (converted to hex digits 0-F) are then read in reverse order (from the last remainder to the first). For instance, decimal 250 becomes $FA_{16}$ after this process.
How to convert hex to decimal?
Converting hex to decimal (also known as hex to integer conversion) involves multiplying each hexadecimal digit by 16 raised to the power of its position index, starting from zero on the far right. For example, to convert $2B$: $(2 \times 16^1) + (11 \times 16^0) = 32 + 11 = 43$. This positional sum method allows for the accurate translation of any hex string into a standard decimal number.
Why use hexadecimal in programming?
Hexadecimal is the standard in programming because it provides a human-readable way to represent binary data. Since $16$ is $2^4$, exactly one hex digit represents four bits (a nibble). This makes it much easier to manage large binary strings; for example, an 8-bit byte can be written as just two hex digits (00 to FF). It is the preferred format for memory addressing, defining RGB colors, and analyzing data at the bit level.
What formulas does the hex calculator use?
Our tool applies the fundamental positional notation formula: $Value = \sum_{i=0}^{n} (d_i \times 16^i)$, where $d$ represents the hex digit value. For arithmetic, it implements standard base-16 logic for carries and borrows. These algorithms are verified against computer science standards to ensure that hexadecimal arithmetic tasks, whether for simple offsets or complex data encoding, are performed with absolute precision.
Disclaimer: This calculator is designed to provide helpful estimates for informational purposes. While we strive for accuracy, financial (or medical) results can vary based on local laws and individual circumstances. We recommend consulting with a professional advisor for critical decisions.