Ohm's Law Calculator
Calculate Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Power in Seconds
Calculate:
Current (I):
Resistance (R):
Please enter the required details and click Calculate.
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Choose which parameter you will calculate (voltage, current, or resistance).
-
Enter the known values using the appropriate units (volts, amps, ohms).
-
Select Click "Calculate" to receive the results utilizing Ohm's Law
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
- Using Milliamps (mA) in the formula without converting to Amps (A), leading to results 1000x too large.
- Confusing Power (Watts) with Current (Amps).
- Forgetting that resistance in a wire increases with heat, which can change your results in high-power applications.
Practical Applications📊
Determine voltage drop to safely choose circuit components.
Determine current flow supply the power required by the components.
Assess resistance values to optimize circuit performance and energy efficiency.
Questions and Answers
What is an Ohm's Law calculator?
An Ohms calculator is a tool that can solve voltage, current, or resistance values using the equation V=IR. You simply need to input two known values, such as voltage and resistance, and it will instantly calculate the third value for you. This is useful in circuit analysis for DC circuits for engineers students and hobbyists, the goal of which is to efficiently design, build, and troubleshoot electrical systems. As long as you use the proper units and the calculator you are using is accurate, like CalcMate, you can use Ohm’s law to get accurate in everything you do in electronics and electrical engineering.
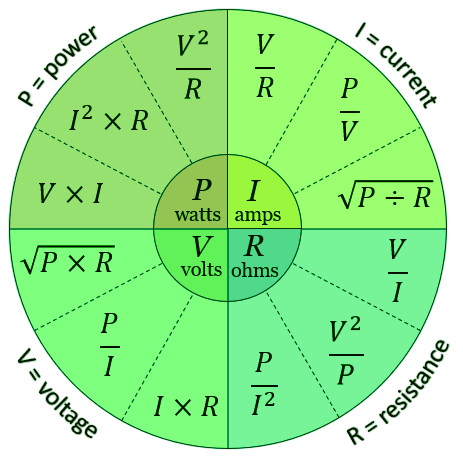
What is the Ohm's Law triangle?
It is a visual mnemonic where V is on top, and I and R are at the bottom. To find one, you cover it with your finger: V=IR, I=V/R, R=V/I.
Can I calculate Power (Watts) here?
Yes! Enter any two values (like Voltage and Current) and the calculator will automatically provide the Power in Watts.
What is resistance?
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current, measured in Ohms (Ω). High resistance means less current flows for a given voltage.
Is Ohm's Law used for AC or DC?
It is primarily for DC. In AC, you must account for Impedance ($Z$), where the logic is $V=IZ$.
How accurate is the Ohms Law calculator?
The calculator utilizes standard formulas ($V = IR$, $I = V / R$, $R = V / I$, $P = VI$) recognized by the IEEE.
What is the formula used in the Ohm's Law solver?
Our calc uses the fundamental formula $V = IR$ (voltage = current $\times$ resistance) and $P = VI$ for power. These principles have been the basis of electrical engineering since 1827.
Disclaimer: This calculator is designed to provide helpful estimates for informational purposes. While we strive for accuracy, financial (or medical) results can vary based on local laws and individual circumstances. We recommend consulting with a professional advisor for critical decisions.