Momentum Calculator
Calculate Linear Momentum and Velocity Changes Instantly
Please select what to calculate.
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Enter mass, velocity or momentum values.
-
Choose units (e.g. kg, m/s).
-
Click "Calculate" and see momentum results.
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
- Treating momentum as a scalar and ignoring the direction of travel.
- Using weight (force) instead of mass.
- Mixing units, such as grams with kilometers per hour.
Practical Applications📊
Examine motion of objects in physics experiments or classroom studies.
Calculate total momentum for collision analysis in engineering or automotive design.
Use with Speed and mass data to analyze dynamics in sports or other vehicle performance.
Questions and Answers
What is a momentum calculator?
A Total momentum calculator is a tool that calculates linear Impulse by inputting mass and velocity into the traditional equation, p = m × v. The momentum equation calculator can calculate total momentum for entire systems or simply for solving an unknown mass or velocity. Using CalcMate, users would simply input their data to arrive at an instantaneous calculation (in kg·m/s) of impulse of motion for anybody in motion. So, whether you're a student of physics or a professional researching, and studying the motion of bodies, then the momentum calculator would be an effective tool to have!
How to calculate momentum with mass and velocity?
To count the momentum, simply enter mass (in kg) and velocity (in m/s) into the momentum calculator. The calculator will use the linear Motion equation (p = m × v) to arrive at momentum (in kg·m/s). For example, a 2000 kg elephant traveling with a velocity of 5 m/s would have a momentum of 10,000 kg·m/s. You will always arrive at accurate solutions to problems for physics projects or in real life examples.
Is momentum a vector quantity?
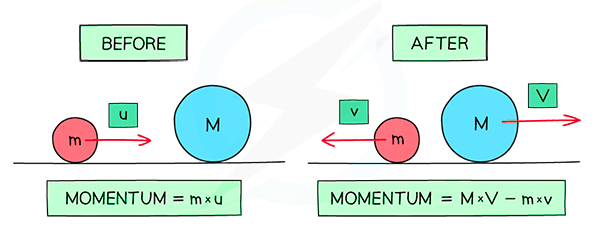
Yes! Momentum is a vector quantity because it relies on velocity and it takes into consideration both the magnitude and direction. Therefore, the momentum vector will be in the same direction as the velocity vector. Direction is also important in physics calculations. For example, to calculate cumulative momentum before and after a collision, you use the mobile calculator to determine impulse of motion before the collision (and the change in direction) to arrive at total impulse of motion.
What are the units for momentum?
The standard SI unit is kilogram-meter per second (kg \cdot m/s). There is no special named unit like the "Joule" for momentum.
How is momentum different from kinetic energy?
Momentum is proportional to velocity (v), while kinetic energy is proportional to velocity squared (v^2). Momentum is a vector; kinetic energy is a scalar.
Can an object have high momentum but low kinetic energy?
Yes, a massive object moving slowly (like a ship) has high momentum but low kinetic energy.
What formula does the Momentum Calculator use?
It uses $p = m \times v$. For a system of objects, it uses the sum: $p_{total} = \sum (m \times v)$. Impulse, or change in momentum, is calculated as $\Delta p = m \times (v_2 - v_1)$.
Disclaimer: This calculator is designed to provide helpful estimates for informational purposes. While we strive for accuracy, financial (or medical) results can vary based on local laws and individual circumstances. We recommend consulting with a professional advisor for critical decisions.