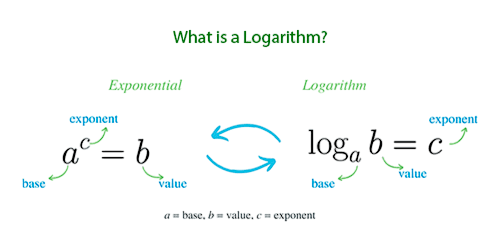Logarithm Calculator
Compute Logarithms for Any Base with Scientific Precision
Calculation Details:
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Enter the argument value.
-
Select or enter the logarithm basis.
-
Press calculate and your result will be displayed.
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
- Attempting to use a base of 1 or 0: The base of a logarithm must be positive and not equal to 1.
- Confusing log (base 10) with ln (natural log, base e).
- Forgetting that log(x + y) is not equal to log(x) + log(y).
Practical Applications📊
Calculate data growth for algorithms based on log base 2.
Calculate exponential decay for physics based on natural log values.
Convert units based on standard log base 10 in chemistry.
Questions and Answers
What is a log calculator?
A log calculator calculates a logarithm for a number with a base specified by the user. A log calculator can be useful when you are solving logarithmic equations, or evaluating a log. For common logarithmic needs, many free tools like CalcMate will give you an accurate answer.
How to use a Logarithm Calculator for base 2?
For log base 2 calculator functions, simply enter your number and set the base to 2, and it will compute your binary logarithms. This is generally useful for computation and information theory.
What makes a logarithmic calculator different from basic ones?
A logarithm calc can accept any basis, including a user defined base and will sometimes even include tools to expand logarithms, or simplify your expression.
How accurate is an online log base 10 calculator?
Online log base 10 calculators use rich algorithms to deliver results with many decimal places, and thus allow for very accurate results in scientific and engineering work.
What is a natural logarithm (ln)?
A natural logarithm is a log with the base e, where e is an irrational constant approximately equal to 2.71828.
What is the common logarithm?
The common logarithm is a log with base 10. It is often written simply as "log" in many textbooks.
Can I calculate the log of a negative number?
In the field of real numbers, logarithms of negative numbers are undefined.
What is the change of base formula?
It is a formula that allows you to calculate any log using natural logs: $\log_b(a) = \ln(a) / \ln(b)$.
What formulas are used in the Logarithm Calculator?
The basic formula is $\log_b(a) = c$, which means that $b^c = a$. For purposes of calculations, it often utilizes a change of base: $\log_b(a) = \log_k(a)/\log_k(b)$, for all $k > 0$ and $k \neq 1$.
Disclaimer: This calculator is designed to provide helpful estimates for informational purposes. While we strive for accuracy, financial (or medical) results can vary based on local laws and individual circumstances. We recommend consulting with a professional advisor for critical decisions.