CPM Calculator
Determine your cost per thousand impressions or calculate the budget and reach for your digital marketing campaigns.
Result
Enter any two values — the third will be calculated automatically (all values in the selected currency).
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Identify which two variables you already have (Cost, Impressions, or CPM).
-
Enter the total budget and the total number of delivered or target impressions.
-
Review the result and use it to compare the efficiency of your marketing channels.
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
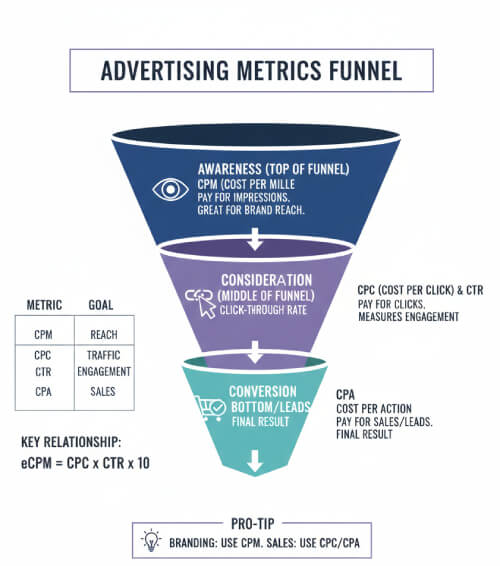
- Confusing CPM with CPC (Cost Per Click); CPM measures views, while CPC measures engagement.
- Forgetting to multiply by 1,000 when performing the calculation manually.
- Using estimated impressions instead of actual delivered impressions when reviewing past campaign performance.
- Neglecting the impact of ad frequency; high frequency can lead to higher CPMs but diminishing returns.
Practical Applications in Media Buying📊
Benchmarking the cost of brand awareness campaigns across multiple social media platforms.
Determining the feasibility of programmatic direct buys versus real-time bidding (RTB) auctions.
Calculating the effective CPM (eCPM) for publishers to analyze the value of their ad inventory.
Forecasting marketing budgets for video ads (YouTube) where CPM rates often differ significantly from display ads.