Friction Force Calculator
Calculate friction using coefficient and normal force.
Calculation Steps
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Select the motion state (static or kinetic).
-
Input the coefficient of friction ($\mu$) for your material pair.
-
Enter the object mass ($m$) and the surface incline angle ($\theta$).
-
Review the calculated friction force and motion prediction.
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
- Confusing mass with weight; weight is m \ g.
- Using the kinetic coefficient to decide if an object starts moving instead of the static one.
- Inputting weight as normal force on inclined surfaces without the $\cos(\theta)$ correction.
- Assuming friction depends on surface area; in the Coulomb model, it does not.
Practical Applications📊
Determine whether an object will remain stationary or slide down an inclined surface.
Estimate the required friction coefficient for vehicle braking or tire grip analysis.
Analyze sliding forces in mechanical assemblies, conveyor systems, or material handling.
Solve university physics problems involving free-body diagrams and inclined planes.
Questions and Answers
What is friction force and why is it important?
Friction force opposes relative motion between two contacting surfaces. It is a central factor in mechanical stability, braking efficiency, and energy loss calculations in engineering.
How do I calculate friction force?
Multiply the coefficient of friction by the normal force: $F = \mu \cdot N$. For inclined planes, the normal force is $N = m \cdot g \cdot \cos(\theta)$.
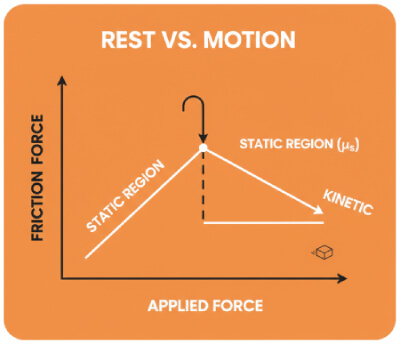
What is the difference between static and kinetic friction?
Static friction prevents the start of motion and can reach a maximum of $\mu_s \cdot N$. Kinetic friction acts during sliding at a constant value $\mu_k \cdot N$, which is usually lower than the static maximum.
How to find the coefficient of friction for different materials?
Coefficients are determined experimentally. Common values range from $0.05$ (ice) to $1.0+$ (high-grip rubber). You can find these values in material reference tables.
Does friction depend on the surface area?
According to the standard Amontons-Coulomb laws, friction is independent of the contact area. It only depends on the nature of the materials and the normal force pressing them together.
What formula does this Friction Force Calculator use?
Our tool implements the classic dry friction model: $F_k = \mu_k \cdot N$ for kinetic and $F_s \leq \mu_s \cdot N$ for static cases. For inclines, it uses $N = m \cdot g \cdot \cos(\theta)$, which is the global standard in physics education and engineering.
Disclaimer: This calculator is designed to provide helpful estimates for informational purposes. While we strive for accuracy, financial (or medical) results can vary based on local laws and individual circumstances. We recommend consulting with a professional advisor for critical decisions.