Pressure Calculator
Accurately Compute Force per Unit Area Online
Enter two of the three fields to calculate the third.
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Provide force magnitude and area size.
-
Specify units like newtons over meters squared.
-
Press compute for immediate output display.
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
- Using weight in kg instead of force in newtons - pressure will be off by ~9.81.
- Entering area in cm² or mm² but selecting m² - result 10⁴–10⁶ too high.
- Confusing pressure with force - pressure = force / area.
- Using kPa when the calculator expects Pa (or vice versa) - off by 1000.
Practical Applications📊
Automotive: Monitoring tire inflation and contact patch load for vehicle safety.
Construction: Calculating the pressure a building foundation exerts on the soil.
Hydraulics: Designing pistons and cylinders that must operate under specific Bar or PSI limits.
Questions and Answers
What does a pressure calculator do?
This tool computes the force exerted per unit area, helping users determine values in pascals or pounds per square inch based on inputs like load and surface dimensions.
How can I find pressure using basic inputs?
To find pressure, divide the applied force by the relevant area; our calculator automates this process for quick, error-free results across various units.
Why calculate psi for mechanical checks?
Computing psi aids in verifying component strength, such as in pipes or engines, by revealing stress levels that inform safety margins.
What is hydrostatic pressure?
It is the pressure exerted by a fluid at equilibrium at any given point within the fluid, due to the force of gravity.
Does pressure increase with depth?
Yes, in fluids, pressure increases as you go deeper because of the weight of the fluid column above you.
Can air pressure calculations vary by altitude?
Yes, atmospheric force decreases with elevation; factor in height above sea level for adjusted barometric readings.
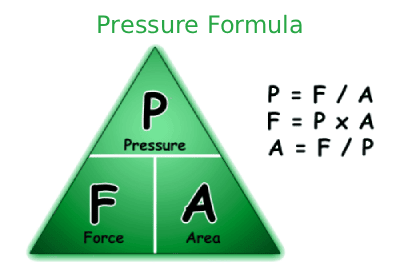
What formulas used in the pressure calculator?
The primary relation is $P = F / A$, where force $F$ in newtons over area $A$ in square meters gives pascals. For hydrostatics, it extends to $P = \rho gh$, with density $\rho$, gravity $g$, and depth $h$. These standards, verified by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), support reliable engineering assessments via CalcMate.
Disclaimer: This calculator is designed to provide helpful estimates for informational purposes. While we strive for accuracy, financial (or medical) results can vary based on local laws and individual circumstances. We recommend consulting with a professional advisor for critical decisions.