Force Calculator
Determine Force, Mass, and Acceleration with Precision
Calculation Examples
📋Steps to Calculate
-
Enter the mass of the object (kg).
-
Enter the acceleration (m/s²).
-
Click the "Calculate" button to see the answer in Newtons.
Mistakes to Avoid ⚠️
- Using weight in kg instead of mass in kg - weight is already force (in newtons).
- Entering acceleration due to gravity when calculating net force - only use it for weight.
- Forgetting to convert g-forces: 2g = 19.6 m/s², not 2 m/s².
- Confusing force with momentum or kinetic energy.
Practical Applications📊
Analyze motion in physics experiments to understand force dynamics.
Calculate impact force for vehicle safety testing.
Measure forces in sports, such as the force of a punch in boxing.
Questions and Answers
What is a force calculator?
A force calculator is a dynamic computational tool that calculates the force acting on an object based on Newton’s second law of motion. In order for the force calculator to compute the force acting on an object, the user simply inputs the mass of the object (in kilograms) and acceleration (in meters per second squared), and the adequate force (in Newtons) will be computed for the user without the complexities of remembering the aspects of physics.
How to calculate force for motion analysis?
It is easy to calculate force for motion studies. Simply plug in the mass of the object in kilograms and the acceleration of that object now expressed in meters per second squared. Calculating the force is needed in analyzing motion in dynamic systems (such as vehicles accelerating down the roadway, or people falling downward through the air in free fall). New tools allow doing accurate calculations and help you to perform accurate and professional calculations for experiments or engineering projects.
What is Newton’s second law of motion?
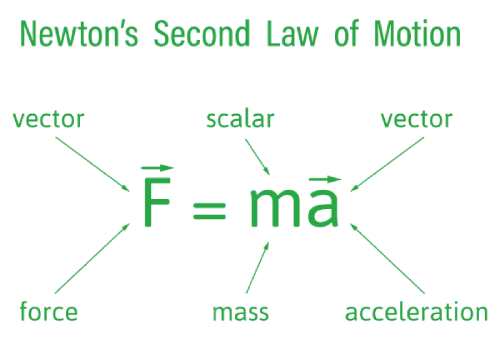
Newton’s Second Law of Motion, as stated by Sir Isaac Newton, says the force acting on an object ($F$) is equal to the mass of the object ($m$) multiplied by the acceleration ($a$): $F = ma$. Newton's Second Law of Motion is one of the fundamental principles of classical mechanics and is accepted by the International System of Units (SI). The equation will calculate the force (in Newtons) if given the object's mass in kilograms and the object's acceleration in meters per second squared.
What is a Newton (N)?
A Newton is the standard unit of force. It equals the force needed to move 1 kg at an acceleration of 1 m/s².
How does mass affect force?
According to $F = ma$, if you double the mass of an object, you need twice as much force to achieve the same acceleration.
Is weight a force?
Yes. Weight is the force exerted on a mass by gravity. You can calculate it by multiplying mass by 9.81.
What happens if acceleration is zero?
If acceleration is zero, the net force is zero. This means the object is either at rest or moving at a perfectly constant velocity.
Why use a force calculator for physics?
The vast majority of the activities of students and enthusiasts studying physics rely on physical force, from studying motion to designing mechanical systems, to learning how forces operate in athletics or vehicles in a car crash. The force calculator is an unmatched tool due to its ability to uniformly calculate forces with one variable, mass, and second variable, acceleration, all of which, based on Isaac Newtons second law can all be accurately displayed in Newtons. For time and error savings, the force calculator is a fantastic tool for physics students and enthusiasts. At the end of the day, the force calculator is always a valuable tool when the data provided is calculated with Newtons second law in mind.
What is contact force?
A contact force is an interaction that occurs only when two objects physically touch. Examples include friction, which opposes motion between surfaces, and the normal force, which prevents objects from sinking into surfaces, like a chair supporting your weight. Unlike non-contact forces such as magnetic or gravitational forces, direct-contact forces require physical interaction.
Disclaimer: This calculator is designed to provide helpful estimates for informational purposes. While we strive for accuracy, financial (or medical) results can vary based on local laws and individual circumstances. We recommend consulting with a professional advisor for critical decisions.